Cardiac Devices¶
Marcus Threadcraft
Types of Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices (CIED)¶
- For Controlling Arrhythmias: Implantable Pulse Generators
- Pacemakers: Anti-bradycardia pacing
- ICDs: Anti-tachycardia pacing and defibrillation
- Biventricular Pacemakers: CRT for ventricular dyssynchrony (LBBB & Heart Failure)
- Loop Recorders: implantable devices for monitoring arrhythmias (most often Afib)
- LVADs: augment cardiac output for end-stage heart failure (not covered here)
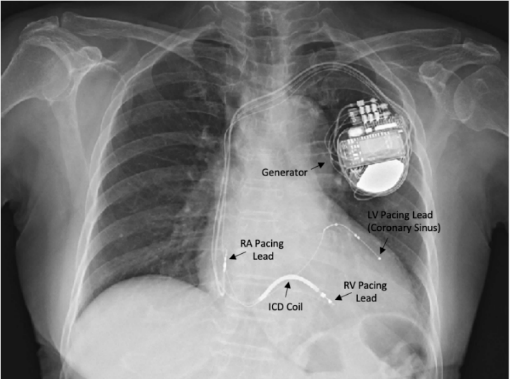
Pacemakers¶
- Provide anti-bradycardia pacing by stimulating myocardium
- Peripheral permanent pacemakers (PPMs)
- SubQ generator, transvenous leads
- Single chamber RV lead
- Dual chamber RV and RA leads
- BiV: RV, RA, and LV (coronary sinus) leads
- Leadless pacemaker
- Implanted generator in RV
Indications
- Symptomatic Bradycardia
- Heart Block: 2nd Degree Type II w/ sx or 3rd Degree
- Sick Sinus Syndrome
- Carotid Sinus Syndrome
- After catheter ablation of AV node for AF
- CRT
Implantable Cardioverter/Defibrillators (ICDs)¶
- Pacing lead + defibrillation coil
- Detect and treat VT/VF v
- Anti-tachycardia pacing (ATP)- attempts to entrain and terminate VT
- Defibrillation If ATP unsuccessful
Indications
- Primary prevention
- HFrEF
- EF \<35% and NYHA II-III or EF \<30% and NYHA I
- Must be >90d from revasc, >40d from MI, and on GDMT
- Arrhythmogenic syndromes
- Arrhythmogenic RV cardiomyopathy, Brugada syndrome, HCM and cardiac sarcoid with specific risk factors
- HFrEF
- Secondary prevention
- Hx VF arrest or VT
- Inducible VT on EP study with history of syncope
Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT)¶
- BiV pacer that coordinates LV/RV contraction through synchronized activation of each ventricle following atrial contraction.
- -P: CRT pacing only
- -D: ICD function
Indications
- Class I: LBBB and QRS≥150 with EF\<35%, NYHA II- IV, on GDMT, NSR
- Class IIa: EF\<35%, NYHA II- IV, on GDMT, NSR AND
- LBBB & QRS 120-149, non-LBBB & QRS≥150, or EF\<35% and expected to require >40% ventricular pacing
Interpreting Pacemaker Codes¶
| 1st Letter | 2nd Letter | 3rd Letter | 4th Letter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A: atrial, V: ventricular, D: dual, O: none, I: inhibition, R: rate-adaptive | Chamber Paced | Chamber Sensed | Response to Sensed Beat | Program Features |
Examples of Common Pacing Modes¶
- VVI: Single RV lead that delivers a beat if no beat sensed. Often used with chronic AF with bradycardia
- DDDR: Senses and paces both the atria and ventricle. If beat not sensed within a predefined interval, beat delivered. R indicates rate responsivity (changes rate based on changes in patient activity)
- Magnet: Paces at a fixed rate without respect to native electrical activity (AOO,VOO,DOO). Deactivates ICD shock. Often used in surgery or at end of life to avoid ICD shocks
Additional Configurations¶
- Epicardial Leads- pacemaker/defibrillator leads attached to outside
of the heart (requires OR) vs traditional transvenous lead
placement, which are inserted in the Cath Lab
- Epicardial Leads generally placed in smaller children or during cardiac surgery with expected need for pacing/defibrillation
- Abandoned leads
- Absolute contraindication to MRI (ungrounded, produces heat and thermal Injury In setting of magnetic field)
Placement Complications¶
- Acute: pocket hematoma, pneumothorax, myocardial perforation, cardiac tamponade, infection, lead displacement or disconnection
- Long-term: secondary device infection, lead fracture (lead lifetime 10-15 years), insulation failure
Last update:
2022-05-29 04:05:22